Abstract
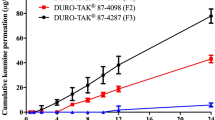
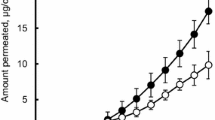
To reduce the adverse effects of aceclofenac that accompanied with oral administration of this drug, transdermal patches in the form of drug-in-adhesive (DIA) patches, containing aceclofenac, were formulated. The effect of formulation factors on the skin permeation of the drug and physical properties of the patch were evaluated using excised rat skins. The optimized patch contained 12 % aceclofenac and 20 % lauryl alcohol in DT-2852 as a pressure-sensitive adhesive. The pharmacokinetic characteristics of the DIA patch were determined after application of the transdermal patches to human volunteers. The calculated relative bioavailability of the aceclofenac DIA patch was 18.2 % compared to oral administration of the drug. The findings of this study suggest that transdermal application of aceclofenac can substitute for oral administration of the drug.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aungst, B.J., N.J. Rogers, and E. Shefter. 1986. Enhancement of naloxone penetration through human skin in vitro using fatty acids, fatty alcohols, surfactants, sulfoxides and amides. The International Journal of Pharmaceutics 33: 225–234.
Bae, J.H., K.E. Choi, S.-C. Chi, and E.-S. Park. 1999. Bioequivalence evaluation of aceclofenac tablets. Korean Journal of Clinical Pharmacy 9: 44–48.
Brogden, R.N., and L.R. Wiseman. 1996. Aceclofenac. A review of its pharmacodynamic properties and therapeutic potential in the treatment of rheumatic disorders and in pain management. Drugs 52: 113–124.
Chedgzoy, P., G. Winckle, and C.M. Heard. 2002. Triclosan: Release from transdermal adhesive formulations and in vitro permeation across human epidermal membranes. The International Journal of Pharmaceutics 235: 229–236.
Cho, S.J., D.R. You, and K.S. Kim. 2001. The effects of enhancers on the transdermal absorption of ketoprofen packs. Yakche Hakhoechi 31: 107–112.
Ghosh, S., and B.B. Barik. 2010. A comparative study on the pharmacokinetics of conventional and sustained-release tablet formulations of aceclofenac in healthy male subjects. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 9: 395–399.
Guyot, M., and F. Fawaz. 2000. Design and in vitro evaluation of adhesive matrix for transdermal delivery of propranolol. The International Journal of Pharmaceutics 204: 171–182.
Kang, W., and E.-Y. Kim. 2008. Simultaneous determination of aceclofenac and its three metabolites in plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 46: 587–591.
Lee, P.J., N. Ahmad, R. Langer, S. Mitragotri, and V.P. Shastri. 2006. Evaluation of chemical enhancers in the transdermal delivery of lidocaine. The International Journal of Pharmaceutics 308: 33–39.
Lee, S.L., C.K. Jeong, S.J. Choi, S.B. Kim, M.H. Lee, G.I. Ko, and D.H. Sohn. 2000. Simultaneous determination of aceclofenac and diclofenac in human plasma by narrowbore HPLC using column-switching. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 23: 775–781.
Narishetty, S.T.K., and R. Panchagnula. 2004. Transdermal delivery of zidovudine: Effect of terpenes and their mechanism of action. The Journal of Controlled Release 95: 367–379.
Rhee, Y.-S., J.-Y. Huh, C.-W. Park, T.-Y. Nam, K.-R. Yoon, S.-C. Chi, and E.-S. Park. 2007. Effects of vehicles and enhancers on transdermal delivery of clebopride. Archives of Pharmacal Research 30: 1155–1161.
Takayama, K., J. Takahara, M. Fujikawa, H. Ichikawa, and T. Nagai. 1999. Formula optimization based on artificial neural networks in transdermal delivery. The Journal of Controlled Release 62: 161–170.
Tan, H.S., and W.R. Pfister. 1999. Pressure-sensitive adhesives for transdermal drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Today 2: 60–69.
Tessari, L., L. Ceciliani, A. Belluati, G. Letizia, U. Martorana, L. Pagliara, A. Pognani, G. Thovez, A. Siclari, G. Torri, L. Solimeno, and E. Montull. 1995. Aceclofenac cream versus piroxicam cream in the treatment of patients with minor traumas and phlogistic affections of soft tissues: A double-blind study. Current Therapeutic Research 56: 702–712.
Thorat, S.P., and S.I. Rane. 2010. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of lecithin (soya and egg) aceclofenac organogels. Journal of Pharmacy Research 3: 1438–1441.
Venkatraman, S., and R. Gale. 1998. Skin adhesives and skin adhesion 1. Transdermal drug delivery systems. Biomaterials 19: 1119–1136.
Yamazaki, R., S. Kawai, T. Matsuzaki, N. Kaneda, S. Hashimoto, T. Yokokura, R. Okamoto, T. Koshino, and Y. Mizushima. 1997. Aceclofenac blocks prostaglandin E2 production following its intracellular conversion into cyclooxygenase inhibitors. The European Journal of Pharmacology 329: 181–187.
Yang, J.-H., Y.-I. Kim, and K.-M. Kim. 2002. Preparation and evaluation of aceclofenac microemulsion for transdermal delivery system. Archives of Pharmacal Research 25: 534–540.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs (#A092018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhee, YS., Nguyen, T., Park, ES. et al. Formulation and biopharmaceutical evaluation of a transdermal patch containing aceclofenac. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 602–607 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0073-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0073-y